UN-Habitat
-
Landmark Partnerships: UN-Habitat collaborates with organizations like C40 Cities to transform urban planning. This highlights its role in fostering partnerships for urban development.
-
UN System Focal Point: UN-Habitat is the central entity within the UN addressing urbanization and human settlements. This emphasizes its authority and scope within the UN system.
-
Mandate for Sustainable Cities: It’s tasked by the UN General Assembly with promoting socially and environmentally sustainable urban areas and ensuring adequate shelter for all. This underscores its core mission and priorities.
-
Inclusive and Resilient Communities: UN-Habitat works to build inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable cities, reflecting a holistic approach to urban development.
-
Urbanization as a Positive Force: The organization promotes urbanization as a tool for reducing inequality, discrimination, and poverty. This frames urbanization as an opportunity for positive change.
-
Three-Tier Structure: UN-Habitat operates with the UN-Habitat Assembly, the Executive Board, and the Committee of Permanent Representatives. This structure allows for broad member state participation and oversight.
-
UN-Habitat Assembly: A universal body with all 193 UN member states, meeting every four years. This enables global representation in setting UN-Habitat’s agenda.
-
Executive Board: Composed of 36 member states, meeting three times a year for operational oversight. This allows for greater accountability.
-
Committee of Permanent Representatives (CPR): Meets twice every four years in an open-ended manner, facilitating continuous engagement.
-
World Habitat Day: First celebrated in 1986, it illustrates the organization’s long-standing commitment to addressing shelter and housing issues. The first theme was “Shelter is My Right”.
Khara Committee
- The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) established the “Dinesh Khara Committee.”
- The committee comprises seven members and is headed by former SBI chairman Dinesh Khara.
- Purpose: To review proposed amendments to the Insurance Act of 1938 and suggest a framework for their implementation through regulations and circulars.
- The committee was formed as the Union government prepares to introduce the Insurance Amendment Bill to Parliament.
- Proposed Amendments: Include increasing the foreign direct investment (FDI) cap in the insurance sector from 74% to 100%, reducing paid-up capital requirements, introducing a composite license system, and streamlining regulatory processes.
- The committee’s role is limited to reviewing proposed changes and implementation; it cannot suggest additional amendments.
- Why It Matters: The Insurance Act of 1938 is the primary regulatory framework for India’s insurance industry and led to IRDAI’s establishment. The Act defines the scope of insurance and regulates relationships between insurers, policyholders, shareholders, and IRDAI. The amendments and their implementation have far-reaching implications for the insurance sector and its stakeholders.
Manikaran
-
Dispute over water transfer: A proposal to transfer hot spring water from Manikaran, a pilgrimage site, to Kasol for a hot bath facility has sparked local opposition.
-
Religious significance: Manikaran is a significant religious site for both Hindus and Sikhs, featuring temples like the Shiva temple and Manikaran Sahib Gurudwara. Its hot springs are believed to have healing properties and are said to be radioactive.
-
Local outrage: Residents fear the plan to use holy water for commercial purposes. They’ve threatened protests and argue the water should be used for development in Manikaran itself.
-
Development vs. preservation: The dispute highlights a clash between development initiatives (a nature park in Kasol) and preservation of religious sites and local traditions.
-
Political involvement: Local politicians, including BJP’s Narotam Thakur and Congress’s Sunder Singh Thakur, are involved in the debate, with accusations of vested interests.
-
Former MP’s opposition: Former MP Maheshwar Singh also voiced opposition, stressing the sacred nature of the water.
-
MLA’s counter-argument: The Kullu MLA defended the proposed development, asserting previous opposition to similar projects.
Digital Brand Guide
- MeitY Launches Digital Brand Identity Manual (DBIM) & CIO Conference 2025: Aimed at harmonizing the government’s digital presence.
- “Gov.In: Harmonisation of Government of India’s Digital Footprint” initiative: Streamlines government websites for easy citizen access.
- Standardized Digital Identity: Creates a unified digital brand for the Government of India, enhancing trust and accessibility.
- DBIM Toolkit: Ensures uniformity through standardized color palettes, typography, and iconography across government platforms.
- Comprehensive Guidelines: Covers websites, mobile apps, and social media, ensuring a seamless user experience.
- Key Components Introduced: DBIM Toolkit, Gov.In CMS Platform, Central Content Publishing System (CCPS), and Social Media Campaign Guidelines.
- Gov.In CMS Platform: Streamlines website management.
- Central Content Publishing System (CCPS): Centralizes content governance, improving transparency and public engagement.
- Social Media Campaign Guidelines: Standardizes digital communication.
- CIO Conference 2025: Focused on DBIM adoption, unified brand identity, and enhanced accessibility.
- User-Centric Approach: Government portals must be user-friendly, accessible, and efficient like private sector websites.
- Viksit Bharat 2047: Contributes to India’s vision by leveraging AI, security, and seamless digital ecosystems.
- Unified Government’s Digital Presence Seeks to establish a standardized and seamless digital presence across government ministries, departments and agencies
Coronal Holes
-
New Study on Coronal Holes: Researchers have accurately measured the thermal and magnetic field properties of solar coronal holes.
-
What are Coronal Holes?: Dark, cooler, less dense regions on the Sun, visible in X-ray and extreme ultraviolet light. They possess open, unipolar magnetic fields.
-
Importance: Crucial for understanding space weather, the interplanetary medium, and potential impacts on Earth.
-
Solar Cycle: Coronal holes are common throughout the Sun’s 11-year cycle, lasting longer during solar minimum.
-
Space Weather Impact: Can disrupt Earth’s ionosphere (affecting radio waves and communications) and impact satellites. Also, recent physics-based study suggests they influence Indian monsoon rainfall.
-
Solar Wind Source: Coronal holes are sources of fast solar wind, streams of charged particles that can cause geomagnetic storms.
-
IIA Study Findings: The Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) analyzed eight years of data from the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO).
-
Key Results:
- No significant latitudinal variation in coronal hole temperature.
- Magnetic field strength increases from the solar equator to the poles.
-
Implications: Constant temperature suggests a deep origin within the Sun. Magnetic field variation hints at formation via superposition of Alfven wave perturbations.
Parkinson’s
- Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting movement.
- It causes nerve cell damage and death in parts of the brain, leading to movement problems, tremors, stiffness, and balance issues.
- The substantia nigra, an area near the brain’s base, is crucial.
- Neurons in this area produce dopamine, a chemical messenger for smooth movement.
- Significant dopamine loss (60-80%) occurs before symptoms appear.
- Dopamine deficiency causes slow movements and tremors.
- Parkinson’s risk increases with age, with an average onset at 60 and slightly higher incidence in males.
- Currently, no blood or imaging tests diagnose Parkinson’s.
- There’s no cure, but treatments manage symptoms.
- A new study identified 24-OHC, a cholesterol metabolite, as a factor fueling harmful protein clump spread in the brain, potentially contributing to the disease.
- Cognitive (thinking and memory) symptoms are common but not universal in Parkinson’s.
AOR: Supreme Court Lawyer
- Advocate-on-Record (AoR) is a specific legal professional authorized to represent clients in the Supreme Court.
- AoRs have exclusive filing and conduct rights in the SC. No other advocate can appear without an AoR’s instruction.
- The Supreme Court holds AoRs fully responsible for the accuracy of petitions, even if drafted by others.
- AoRs are subject to specific requirements for registration: enrollment with a State Bar Council, 4+ years experience, 1-year training under a senior AoR, Supreme Court examination, Delhi office requirement, and clerk employment.
- AoRs receive a unique identification number and are solely authorized to file Vakalatnamas (representation documents) in the SC.
- AoRs are personally liable for court fees.
- All procedural aspects (drafting, filing) must be completed by the AoR with a registered clerk’s assistance.
- The SC sends notices/orders/correspondence directly to the AoR.
- This system differs from other High Courts in India.
- The Supreme Court’s power to create AoR rules stems from Article 145(1) of the Constitution.
- Candidates get five attempts for the AoR exam.
Majorana Fermion
- Microsoft has released Majorana 1, the world’s first quantum chip built on a topological core, on February 19,2025.
- CEO Satya Nadella calls it a leap in computing unlocked by new materials (top conductors).
- Majorana 1 is designed to make quantum computing more practical, faster, and reliable.
- It leverages a topoconductor, creating more stable qubits less prone to losing information.
- It relies on Majorana fermions, theorized in 1937.
- The chip uses indium arsenide and aluminum to create Microsoft’s “world’s first topoconductor.”
- This could allow quantum computers to scale to millions of qubits.
- Potential applications include designing better medicines, reducing pollution, and creating self-repairing materials.
- Majorana 1 is powered by a Topological Core designed to scale to a million qubits on a single chip.
- The first chip features only eight qubits, but Microsoft plans to scale rapidly.
- Quantum computing uses quantum mechanics to solve complex problems faster than classical computers.
- Qubits can exist in states 0, 1, or both simultaneously (superposition), enabling faster solutions.
- Qubits are fragile and prone to errors, which Majorana 1 aims to address.
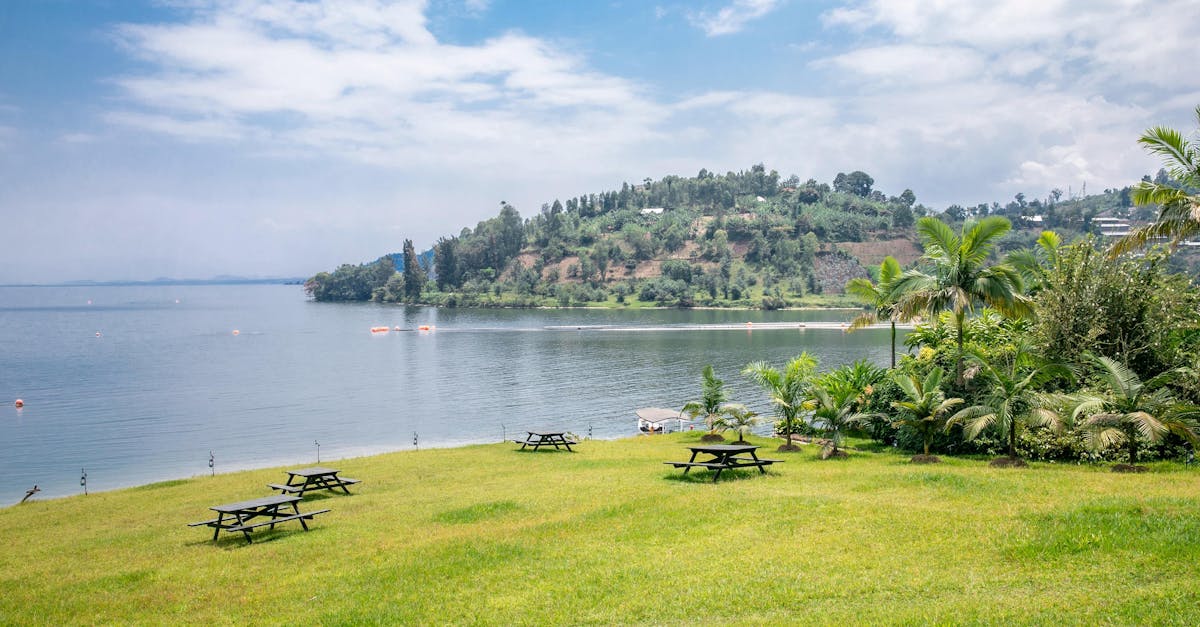
Kivu Lake
- Lake Kivu is a large lake in East Africa, bordering the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and Rwanda.
- It’s one of the great lakes of East Africa and Rwanda’s largest, situated in the Albertine Rift.
- It lies at 1,460 meters above sea level and covers 1,040 square miles.
- 58% of the lake’s water is in the DRC, and the rest is in Rwanda.
- It flows into the Rusizi River, which then flows into Lake Tanganyika.
- Idjwi Island, one of the largest inland islands globally, is located in the lake.
- Lake Kivu is a significant source of fish for Rwanda.
- Recent conflict in Goma, DRC, affecting the region around Lake Kivu.
