-
Destruction of Key Research Centre: The world’s only research centre dedicated to mycetoma, located in Sudan, has been destroyed due to the ongoing war. This is a major setback for research and treatment efforts.
-
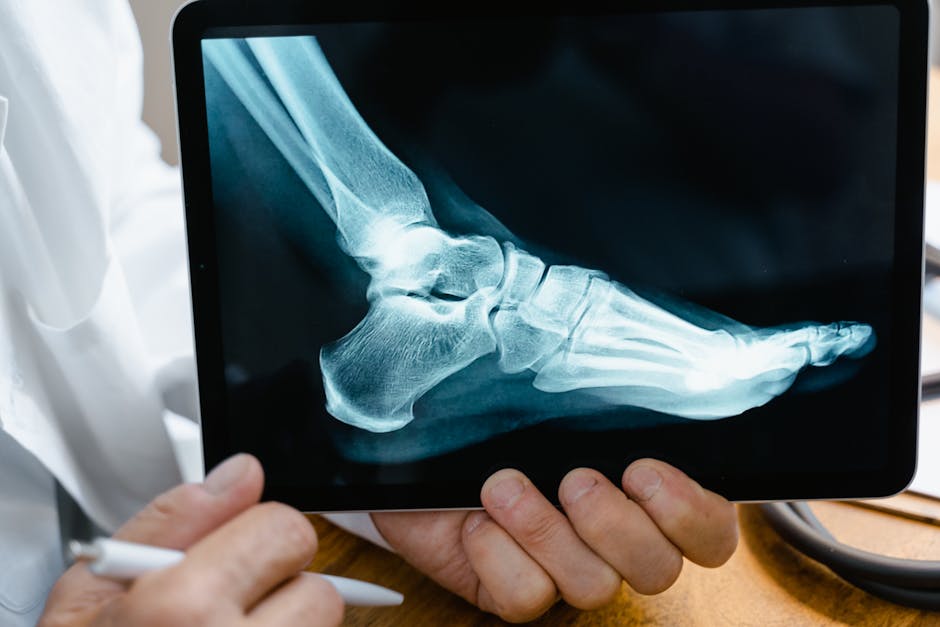
What is Mycetoma? It’s a chronic, destructive infectious disease affecting skin, tissues, and bone, primarily in developing countries.
-
“Madura Foot” Origin: Initially reported in Madurai, India in the mid-19th century.
-
Cause: Neglected tropical disease caused by various fungi or bacteria.
-
Who is Affected: Young adult males (15-30 years) in developing nations are most susceptible.
-
Geographic Distribution: Prevalent in the “Mycetoma belt” – tropical and subtropical regions with dry seasons, including Venezuela, Chad, Ethiopia, India, Sudan, and Yemen.
-
Transmission: Enters the body through trauma, like thorn pricks, often affecting barefoot manual workers.
-
Symptoms: Firm, painless masses under the skin (usually on the foot), which can grow, develop sores, and discharge colored grains. If untreated, it leads to deformities, blood infections, and destruction of muscle and bone.
-
Treatment: Bacterial mycetoma is treated with antibiotics; fungal mycetoma requires antifungals and surgery.
-
Causative Agents Source: Bacteria and fungi found in soil, plant matter, and water.