The Chalukya dynasty was an Indian royal dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty, known as the “Badami Chalukyas”, ruled from Vatapi (modern Badami) from the middle of the 6th century. The Badami Chalukyas began to assert their independence at the decline of the Kadamba kingdom of Banavasi and rapidly rose to prominence during the reign of Pulakeshin II. After the death of Pulakeshin II, the Eastern Chalukyas became an independent kingdom in the eastern Deccan. They ruled from Vengi until about the 11th century. In the western Deccan, the rise of the Rashtrakutas in the middle of the 8th century eclipsed the Chalukyas of Badami before being revived by their descendants, the Western Chalukyas, in the late 10th century. These Western Chalukyas ruled from Kalyani (modern Basavakalyan) until the end of the 12th century. The rule of the Chalukyas marks an important milestone in the history of South India and a golden age in the history of Karnataka. The political Atmosphere in South India shifted from smaller kingdoms to large empires with the ascendancy of Badami Chalukyas. A Southern India-based kingdom took control and consolidated the entire region between the Kaveri and the Narmada rivers. The rise of this empire saw the birth of efficient administration, overseas Trade and Commerce and the development of new style of architecture called “Chalukyan architecture”. Kannada literature, which had enjoyed royal support in the 9th century Rashtrakuta court found eager patronage from the Western Chalukyas in the Jain and Veerashaiva traditions. The 11th century saw the birth of Telugu literature under the patronage of the Eastern Chalukyas.
Chalukayas of badami
In the 6th century, with the decline of The Gupta Dynasty and their immediate successors in northern India, major changes began to happen in the area south of the Vindhyas – the Deccan and Tamilaham. The age of small kingdoms had given way to large empires in this region. The Chalukya dynasty was established by Pulakeshin I in 543. Pulakeshin I took Vatapi (modern Badami in Bagalkot district, Karnataka) under his control and made it his capital. Pulakeshin I and his descendants are referred to as “Chalukyas of Badami”. They ruled over an empire that comprised the entire state of Karnataka and most of Andhra Pradesh in the Deccan.
Chalukyas of kalyani
The Chalukyas revived their fortunes in 973 after over 200 years of dormancy when much of the Deccan was under the rule of The Rashtrakutas. The genealogy of the kings of this empire is still debated. One theory, based on contemporary literary and inscriptional evidence plus the finding that the Western Chalukyas employed titles and names commonly used by the early Chalukyas, suggests that the Western Chalukya kings belonged to the same family line as the illustrious Badami Chalukya dynasty of the 6th century while other Western Chalukya inscriptional evidence indicates they were a distinct line unrelated to the Early Chalukyas.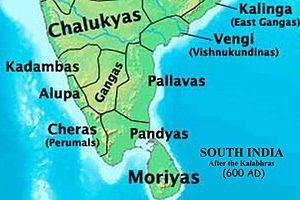
Chalukyas of vengi
Chalukyas of Vengi Main ARTICLE: Eastern Chalukyas Pulakeshin II conquered the eastern Deccan, corresponding to the coastal districts of modern Andhra Pradesh in 616, defeating the remnants of the Vishnukundina kingdom. He appointed his brother Kubja Vishnuvardhana as Viceroy in 621. Thus the Eastern Chalukyas were originally of Kannada stock. After the death of Pulakeshin II, the Vengi Viceroyalty developed into an independent kingdom and included the region between Nellore and Visakhapatnam.
Architecture during chalukyas
The Badami Chalukya era was an important period in the development of South Indian architecture. The kings of this dynasty were called Umapati Varlabdh and built many temples for the Hindu god Shiva. Their style of architecture is called “Chalukyan architecture” or “Karnata Dravida architecture”. Nearly a hundred monuments built by them, rock cut (cave) and structural, are found in the Malaprabha river basin in modern Bagalkot district of northern Karnataka. The building material they used was a reddish-golden Sandstone found locally. These cave temples are basically excavations, cut out of the living rock sites they occupy. They were not build as their structural counterparts were, rather created by a special technique known as “subtraction” and are basically sculptural. Though they ruled a vast empire, the Chalukyan workshops concentrated most of their temple building activity in a relatively small area within the Chalukyan heartland – Aihole, Badami, Pattadakal and Mahakuta in modern Karnataka state.
Their temple building activity can be categorised into three phases. The early phase began in the last quarter of the 6th century and resulted in many cave temples, prominent among which are three elementary cave temples at Aihole (one Vedic, one Jain and one Buddhist which is incomplete), followed by four developed cave temples at Badami (of which cave 3, a Vaishnava temple, is dated accurately to 578 CE). These cave temples at Badami are similar, in that, each has a plain exterior but an exceptionally well finished interior consisting of a pillared verandah, a columned hall (mantapa) and a cella (shrine, cut deep into rock) which contains the deity of worship. In Badami, three caves temples are Vedic and one in Jain. The Vedic temples contain large well sculpted images of Harihara, Mahishasuramardhini, Varaha, Narasimha, Trivikrama, Vishnu seated on Anantha (the snake) and Nataraja (dancing Shiva).
The second phase of temple building was at Aihole (where some seventy structures exist and has been called “one of the cradles of Indian Temple Architecture“[109]) and Badami. Though the exact dating of these temples has been debated, there is consensus that the beginnings of these constructions are from c. 600.These are the Lad Khan Temple (dated by some to c. 450 but more accurately to 620) with its interesting perforated stone windows and sculptures of river goddesses; the Meguti Jain Temple (634) which shows progress in structural design; the Durga Temple with its northern Indian style tower (8th century) and experiments to adapt a Buddhist Chaitya design to a brahminical one (its stylistic framework is overall a hybrid of north and south Indian styles.); the Huccimalli Gudi Temple with a new inclusion, a vestibule, connecting the sanctum to the hall. Other dravida style temples from this period are the Naganatha Temple at Nagaral; the Banantigudi Temple, the Mahakutesvara Temple and the Mallikarjuna Temple at Mahakuta; and the Lower Sivalaya Temple, the Malegitti Sivalaya Temple (upper) and the Jambulingesvara Temple at Badami. Located outside the Chalukyan architectural heartland, 140 km south-east of Badami, with a structure related to the Early Chalukya style is the unusual Parvati Temple at Sanduru which dates to the late 7th century. It is medium-sized, 48 ft long and 37 ft wide. It has a nagara (north Indian) style vimana (tower) and dravida (south Indian) style parts, has no mantapa (hall) and consists of an antarala (vestibule) crowned with a barrel vaulted tower (sukhanasi). The “staggered” base plan of the temple became popular much later, in the 11th century.
The structural temples at Pattadakal, built in the 8th century and now a UNESCO World Heritage Site, marks the culmination and mature phase of Badami Chalukyan architecture. The Bhutanatha group of temples at Badami are also from this period. There are ten temples at Pattadakal, six in southern dravida style and four in the northern nagara style. Well known among these are the Sangamesvara Temple (725), the Virupaksha Temple (740–745) and the Mallikarjuna Temple (740–745) in the southern style. The Papanatha temple (680) and Galaganatha Temple (740) are early attempts in the nagara – dravida fusion style. Inscriptional evidence suggests that the Virupaksha and the Mallikarjuna Temples were commissioned by the two queens of King Vikramaditya II after his military success over the Pallavas of Kanchipuram. Some well known names of Chalukyan architects are Revadi Ovajja, Narasobba and Anivarita Gunda.
The reign of Western Chalukyas was an important period in the development of Deccan Architecture. Their architecture served as a conceptual link between the Badami Chalukya Architecture of the 8th century and the Hoysala architecture popularised in the 13th century.The centre of their cultural and temple-building activity lay in the Tungabhadra region of modern Karnataka state, encompassing the present-day Dharwad district; it included areas of present-day Haveri and Gadag districts. Here, large medieval workshops built numerous monuments.These monuments, regional variants of pre-existing dravida temples, defined the Karnata dravida tradition.,
The Chalukyas were a dynasty that ruled over large parts of southern and central India from the 6th to the 12th centuries. They were originally from Vatapi (modern Badami), in the present-day state of Karnataka. The Chalukyas were divided into two branches: the Western Chalukyas and the Eastern Chalukyas. The Western Chalukyas ruled over the Deccan Plateau, while the Eastern Chalukyas ruled over the region around Vengi (modern Andhra Pradesh).
The Chalukyas were a powerful and influential dynasty. They were patrons of art, architecture, and literature. They built many temples and palaces, and their art and architecture is considered to be some of the finest in India. The Chalukyas also made significant contributions to literature. They wrote many works in Sanskrit, Kannada, and Telugu.
The Chalukyas were eventually overthrown by Cholas/”>The Cholas in the 12th century. However, their legacy continues to this day. Their art, architecture, and literature are still admired and studied by people all over the world.
Origin and early history of the Chalukyas
The Chalukyas were originally from Vatapi (modern Badami), in the present-day state of Karnataka. They were a branch of the Kshatriya caste, and their founder was Pulakesin I. Pulakesin I was a powerful ruler who conquered much of the Deccan Plateau. He was succeeded by his son, Kirtivarman I, who further expanded the Chalukya empire.
Rule of the Western Chalukyas
The Western Chalukyas reached their peak under the reign of Vikramaditya I (655-680 CE). Vikramaditya I was a great conqueror who defeated the Pallavas and the Pandyas. He also built many temples and palaces, and his reign is considered to be a golden age for the Chalukyas.
After Vikramaditya I, the Western Chalukya empire began to decline. This was due to a number of factors, including internal strife and external threats from the Rashtrakutas and the Cholas. The Western Chalukyas were eventually overthrown by the Cholas in 1190 CE.
Rule of the Eastern Chalukyas
The Eastern Chalukyas were a branch of the Chalukya dynasty that ruled over the region around Vengi (modern Andhra Pradesh). They were founded by Vishnuvardhana in 610 CE. The Eastern Chalukyas reached their peak under the reign of Narasimha II (695-726 CE). Narasimha II was a great conqueror who defeated the Pallavas and the Pandyas. He also built many temples and palaces, and his reign is considered to be a golden age for the Eastern Chalukyas.
After Narasimha II, the Eastern Chalukya empire began to decline. This was due to a number of factors, including internal strife and external threats from the Cholas and the Rashtrakutas. The Eastern Chalukyas were eventually overthrown by the Cholas in 1070 CE.
Art and architecture of the Chalukyas
The Chalukyas were patrons of art and architecture. They built many temples and palaces, and their art and architecture is considered to be some of the finest in India. The Chalukya temples are known for their intricate carvings and sculptures. The Chalukya palaces are known for their elegant architecture.
Literature of the Chalukyas
The Chalukyas also made significant contributions to literature. They wrote many works in Sanskrit, Kannada, and Telugu. The Chalukya literature is known for its beauty and its rich content.
Decline and fall of the Chalukyas
The Chalukyas were eventually overthrown by the Cholas in the 12th century. However, their legacy continues to this day. Their art, architecture, and literature are still admired and studied by people all over the world.
Legacy of the Chalukyas
The Chalukyas were a powerful and influential dynasty that ruled over large parts of southern and central India for over 600 years. They were patrons of art, architecture, and literature, and their contributions to these fields are still admired today. The Chalukyas were also skilled warriors who expanded their empire through conquest. However, their empire eventually declined and fell to the Cholas in the 12th century. Despite their fall, the Chalukyas left a lasting legacy on Indian history and culture.
Here are some frequently asked questions and short answers about the UKPCS Mains exam:
-
What is the UKPCS Mains exam?
The UKPCS Mains exam is a national-level competitive exam conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) for the recruitment of officers to the Indian Administrative Service (IAS), Indian Foreign Service (IFS), Indian Police Service (IPS), and other Group A and Group B Services of the Government of India. -
What are the eligibility criteria for the UKPCS Mains exam?
To be eligible for the UKPCS Mains exam, candidates must: - Be a citizen of India
- Have a Bachelor’s degree from a recognized university
-
Be between the ages of 21 and 32 years on the 1st of January of the year in which the exam is conducted
-
What are the subjects for the UKPCS Mains exam?
The UKPCS Mains exam consists of two papers: - Paper I: General Studies I
- Paper II: General Studies II
Paper I consists of questions on topics such as Indian Polity and Governance, Indian economy, General Knowledge, Current Affairs, and History of India.
Paper II consists of questions on topics such as Geography of India, Society/”>Indian Society, Culture and Values, Environment and ECOLOGY, and Science and Technology.
- How is the UKPCS Mains exam conducted?
The UKPCS Mains exam is conducted in two stages: - Preliminary Examination
- Main Examination
The Preliminary Examination is a two-hour objective-type exam consisting of two papers:
* Paper I: General Studies I
* Paper II: General Studies II
The Main Examination is a three-day exam consisting of nine papers:
* Paper I: General Studies I
* Paper II: General Studies II
* Paper III: General Studies III
* Paper IV: General Studies IV
* Paper V: Essay
* Paper VI: Optional Paper I
* Paper VII: Optional Paper II
* Paper VIII: Optional Paper III
* Paper IX: Optional Paper IV
- What is the syllabus for the UKPCS Mains exam?
The syllabus for the UKPCS Mains exam is as follows:
Paper I: General Studies I
* Indian Polity and Governance
* Indian Economy
* General Knowledge
* Current Affairs
* History of India
Paper II: General Studies II
* Geography of India
* Indian Society, Culture and Values
* Environment and Ecology
* Science and Technology
Paper III: General Studies III
* Indian Constitution
* Indian Legal System
* Public Administration
* International Relations
Paper IV: General Studies IV
* Defence and Security
* Science and Technology
* Economic Development
* Social Justice and Empowerment
Paper V: Essay
* The essay paper is a compulsory paper for all candidates. The essay paper will be of 200 marks and will be of 3 hours duration. The essay paper will be on a general topic of national or international importance.
Paper VI: Optional Paper I
* Candidates can choose any one of the following subjects as their optional paper:
* History
* Geography
* Economics
* Political Science
* Public Administration
* Sociology
* Psychology
* Anthropology
* Philosophy
* Commerce
* Accountancy
* Business Administration
* Mathematics
* Statistics
* Physics
* Chemistry
* Biology
* Biotechnology
* Computer Science
* Engineering
Paper VII: Optional Paper II
* Candidates can choose any one of the following subjects as their optional paper:
* History
* Geography
* Economics
* Political Science
* Public Administration
* Sociology
* Psychology
* Anthropology
* Philosophy
* Commerce
* Accountancy
* Business Administration
* Mathematics
* Statistics
* Physics
* Chemistry
* Biology
* Biotechnology
* Computer Science
* Engineering
Paper VIII: Optional Paper III
* Candidates can choose any one of the following subjects as their optional paper:
* History
* Geography
* Economics
* Political Science
* Public Administration
* Sociology
* Psychology
* Anthropology
* Philosophy
* Commerce
* Accountancy
* Business Administration
* Mathematics
* Statistics
* Physics
* Chemistry
* Biology
* Biotechnology
* Computer Science
* Engineering
Paper IX: Optional Paper IV
* Candidates can choose any one of the following subjects as their optional paper:
* History
* Geography
* Economics
* Political Science
* Public Administration
* Sociology
* Psychology
* Anthropology
* Philosophy
* Commerce
* Accountancy
* Business Administration
* Mathematics
* Statistics
* Physics
* Chemistry
* Biology
* Biotechnology
* Computer Science
* Engineering
- What are the marking schemes for the UKPCS Mains exam?
The marking scheme for the UKPCS Mains exam is as
The following are some MCQs on the topics of Indian history, politics, and economics, without mentioning the topic of Chalukyas:
-
Which of the following is not a major river in India?
(A) The Ganges
(B) The Indus
(C) The Brahmaputra
(D) The Narmada -
Which of the following is not a major mountain range in India?
(A) The Himalayas
(B) The Vindhyas
(C) The Satpuras
(D) The Western Ghats -
Which of the following is not a major language spoken in India?
(A) Hindi
(B) Bengali
(C) Tamil
(D) Telugu -
Which of the following is not a major religion practiced in India?
(A) Hinduism-2/”>Hinduism
(B) Islam
(C) Christianity
(D) Sikhism -
Which of the following is not a major political party in India?
(A) The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)
(B) The Indian National Congress (INC)
(C) The Communist Party of India (Marxist) (CPI(M))
(D) The All India Trinamool Congress (TMC) -
Which of the following is not a major economic sector in India?
(A) agriculture
(B) Industry
(C) Services
(D) Tourism -
Which of the following is not a major export product of India?
(A) Software
(B) Gems and jewelry
(C) Pharmaceuticals
(D) Tea -
Which of the following is not a major import product of India?
(A) Crude oil
(B) Gold
(C) Iron Ore
(D) Coal -
Which of the following is not a major trade partner of India?
(A) The United States
(B) China
(C) Japan
(D) Germany -
Which of the following is not a major foreign Investment destination in India?
(A) The United States
(B) China
(C) Japan
(D) the United Kingdom
These are just a few examples of MCQs that can be asked on the topics of Indian history, politics, and economics. There are many other possible questions that could be asked, so it is important to be familiar with the material in order to do well on the exam.