<–2/”>a >Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object and thus in contrast to on-site observation.
In current usage, the term “remote sensing” generally refers to the use of satellite- or aircraft-based sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth, including on the surface and in the Atmosphere and Oceans, based on propagated signals.
Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geography, land surveying and most Earth Science disciplines for example, hydrology, ECOLOGY, Oceanography, glaciology, geology.It also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications.
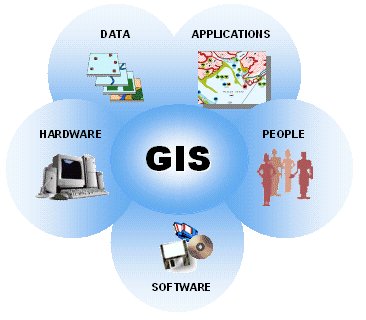
GIS
Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer based application of technology involving spatial and attributes information to act as a decision support tool.
It keeps information in different layers and generates various combinations pertaining to the requirement of the decision-making. In the recent times, GIS has emerged as an effective tool in management of disasters since, geo-spatial data and socio-economic information need to be amalgamated for the better DECISION MAKING in handling a disaster or to plan for tackling a disaster in a better way.
Applications:
The different line departments and agencies who are stakeholders in the disaster management process could utilize GIS. Some basic hardware like computer system, printer, Network systems, along with GIS Software is required to set up the GIS in any organisation.
Objectives:
The prime objectives of developing the GIS Database are to help disaster managers at State, District and Block level for:
- i) Pre-disaster planning and preparedness
- ii) Prediction and early warning
iii) Damage assessment and relief management
GIS combines layers of information on various themes to enable the managers to take the most appropriate decisions under the given circumstances. For disaster management, a GIS database could be a useful managerial tool for various reasons, some of which are as under:
- Disaster Managers could generate maps both at micro and macro level indicating vulnerability to different extents under different threat perceptions.
- Locations likely to remain unaffected or remain comparatively safe could be identified.
- Alternate routes to shelters, camps, and important locations in the event of disruption of normal surface Communication could be worked out.
- Smooth rescue and evacuation operations could be properly planned.
- Rehabilitation and post-disaster reconstruction works could be properly organized.
- Locations suitable for construction of shelters, godowns, housing colonies, etc. can be scientifically identified.
- Areas where no construction should be taken up or existing habitations require relocation could be identified.
Hydrology
Remote sensing of hydrologic processes can provide information on locations where in situ sensors may be unavailable or sparse. It also enables observations over large spatial extents. Many of the variables constituting the terrestrial water balance, for example surface water storage, Soil moisture, Precipitation, evapotranspiration, and snow and ice, are measurable using remote sensing at various spatial-temporal resolutions and accuracies. Sources of remote sensing include land-based sensors, airborne sensors and satellite sensors, which can capture microwave, thermal and near-infrared data or use LIDAR.
Weather forecasting and Ecology
Many ecological research projects would benefit from the creation of a GIS to explore spatial relationships within and between the data. In particular, while some projects can be done without using a GIS, many will be greatly enhanced by using it (click here for some examples of research projects which have used GIS).
The very act of creating a GIS will make you think about the spatial relationships within your data, and will help you formulate hypotheses to test or suggest new ones to explore. In addition, thinking about your data in a spatial manner will help you identify potential spatial issues and/or biases with your data.
GIS can also be used to make measurements and carry out calculations which would otherwise be very difficult. For example, a GIS can be used to work out how much of your study area consists of a specific habitat type, or how much of it is over 1,000m high, or has a gradient greater than 5º, and so on. Similarly, a GIS can be used to calculate the size of the home range of an individual or the total area occupied by a specific species or how long your survey tracks are, or how much survey effort was put into different parts of your study area.
GIS can also be used to link data together in the way that is needed for statistical analysis. For example, many statistical packages require all your data to be in a single table, with one line per sample and then information about that sample and the location where it came from in different columns or fields. A GIS provides you with a way to easily create such tables and populate it with information, such as the altitude at each location, the gradient of slope and the direction it faces, from other data sets. This makes preparing your data for statistical analysis much simpler.
,
Remote sensing and Geographic Information System (GIS) are two powerful tools that can be used to collect, store, analyze, and visualize data. Remote sensing uses satellites and other sensors to collect data about the Earth’s surface, while GIS uses computers to store, analyze, and visualize spatial data.
These two technologies can be used together to solve a wide range of problems in a variety of fields. Some of the most common applications of remote sensing and GIS include:
- agriculture: Remote sensing can be used to monitor crop Growth, identify areas of drought or disease, and assess crop yields. GIS can be used to plan and manage agricultural land, track the movement of pests and diseases, and assess the impact of Climate change on agriculture.
- Archaeology: Remote sensing can be used to locate and map archaeological sites, identify features of interest, and assess the impact of development on archaeological sites. GIS can be used to manage archaeological data, create maps of archaeological sites, and analyze the distribution of archaeological sites.
- Atmospheric science: Remote sensing can be used to monitor air quality, track the movement of pollutants, and assess the impact of Climate Change on the atmosphere. GIS can be used to model the movement of air pollutants, predict the Impact Of Climate Change on air quality, and develop strategies for air quality management.
- Biodiversity-2/”>Biodiversity: Remote sensing can be used to monitor the distribution of plant and animal species, identify areas of biodiversity hotspots, and assess the impact of development on biodiversity. GIS can be used to manage biodiversity data, create maps of biodiversity hotspots, and analyze the distribution of biodiversity.
- Coastal zone management: Remote sensing can be used to monitor coastal erosion, identify areas of pollution, and assess the impact of development on coastal areas. GIS can be used to plan and manage coastal development, track the movement of pollutants, and assess the impact of climate change on coastal areas.
- Disaster management: Remote sensing can be used to monitor natural disasters, such as floods, Earthquakes, and wildfires, and assess the damage caused by disasters. GIS can be used to plan and manage disaster response and recovery, track the movement of people and Resources, and assess the impact of disasters on communities.
- Ecology: Remote sensing can be used to monitor the Health of Ecosystems, identify areas of Environmental Degradation, and assess the impact of climate change on ecosystems. GIS can be used to manage ecological data, create maps of ecosystems, and analyze the distribution of ecosystems.
- Education: Remote sensing and GIS can be used to teach students about geography, environmental science, and other subjects. GIS can be used to create interactive maps and visualizations that help students understand complex spatial data.
- Environmental monitoring: Remote sensing can be used to monitor air quality, water quality, land use, and other environmental conditions. GIS can be used to track the movement of pollutants, assess the impact of development on the Environment, and develop strategies for environmental protection.
- Forest management: Remote sensing can be used to monitor forest cover, identify areas of deforestation, and assess the impact of forest fires. GIS can be used to plan and manage forest management, track the movement of people and resources, and assess the impact of climate change on forests.
- Geography: Remote sensing and GIS can be used to create maps and visualizations that help people understand the Earth’s surface. GIS can be used to track the movement of people and resources, assess the impact of development on the environment, and develop strategies for Sustainable Development.
- Geology: Remote sensing can be used to map geological features, such as faults, Volcanoes-2/”>Volcanoes, and mineral deposits. GIS can be used to track the movement of tectonic plates, assess the risk of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, and develop strategies for mineral exploration.
- Geomorphology: Remote sensing can be used to map Landforms, such as Mountains, valleys, and rivers. GIS can be used to track the movement of Glaciers, assess the impact of erosion and sedimentation, and develop strategies for land management.
- Land use planning: Remote sensing can be used to map land use, identify areas of development, and assess the impact of development on the environment. GIS can be used to plan and manage land use, track the movement of people and resources, and assess the impact of climate change on land use.
- Law enforcement: Remote sensing can be used to monitor crime, identify areas of high crime, and track the movement of criminals. GIS can be used to analyze crime data, develop strategies for crime prevention, and assess the impact of crime on communities.
- Marine science: Remote sensing can be used to map the ocean floor, identify areas of marine life, and assess the impact of climate change on the ocean. GIS can be used to track the movement of marine life, assess the risk of oil spills and other marine disasters, and develop strategies for marine conservation.
- Natural Resources management: Remote sensing can be used to monitor natural resources, such as forests, water, and Minerals. GIS can be used to plan and manage natural resources, track the movement of people and resources,
Remote sensing is the science of obtaining information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with it. Remote sensing data can be used to map and monitor land cover, track changes in the environment, and study natural and human-made phenomena.
GIS is a computer system for capturing, storing, analyzing, and displaying spatial or geographic data. GIS can be used to create maps, analyze spatial relationships, and model spatial processes.
Here are some frequently asked questions about remote sensing and GIS:
- What are the different types of remote sensing data?
There are two main types of remote sensing data: passive and active. Passive remote sensing data is collected when the sensor detects energy that is naturally emitted by the Earth or its atmosphere. Active remote sensing data is collected when the sensor emits energy and then detects the energy that is reflected or backscattered by the Earth or its atmosphere.
- What are the different types of GIS data?
There are two main types of GIS data: vector and raster. Vector data is represented by points, lines, and polygons. Raster data is represented by a grid of cells.
- What are the benefits of using remote sensing and GIS?
Remote sensing and GIS can be used to:
- Map and monitor land cover
- Track changes in the environment
- Study natural and human-made phenomena
- Plan and manage resources
- Make decisions about land use
-
Provide emergency response
-
What are the limitations of using remote sensing and GIS?
The limitations of using remote sensing and GIS include:
- The cost of acquiring and processing remote sensing data
- The complexity of GIS software
- The need for specialized training to use remote sensing and GIS
-
The potential for data errors
-
What are some examples of how remote sensing and GIS are used?
Remote sensing and GIS are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Agriculture: Remote sensing and GIS can be used to monitor crop yields, identify areas of drought Stress, and plan Irrigation systems.
- Forestry: Remote sensing and GIS can be used to map forests, track deforestation, and monitor forest health.
- Urban planning: Remote sensing and GIS can be used to map land use, track changes in development, and plan for future growth.
- Environmental monitoring: Remote sensing and GIS can be used to monitor air quality, water quality, and land degradation.
-
Disaster response: Remote sensing and GIS can be used to assess damage after a disaster, plan relief efforts, and monitor recovery.
-
What are the future trends in remote sensing and GIS?
The future trends in remote sensing and GIS include:
- The development of new remote sensing technologies, such as hyperspectral and LiDAR sensors
- The development of more powerful and user-friendly GIS software
- The integration of remote sensing and GIS with other technologies, such as Social Media and big data
- The use of remote sensing and GIS to address global challenges, such as climate change and Food Security
-
Remote sensing is the science and technology of acquiring and interpreting data from a distance. It is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
-
Agriculture: Remote sensing can be used to monitor crop growth, identify areas of drought or disease, and assess crop yields.
- Forestry: Remote sensing can be used to map forests, monitor deforestation, and assess the health of forests.
- Water Resources: Remote sensing can be used to map water bodies, monitor water quality, and assess water resources.
- Environmental monitoring: Remote sensing can be used to monitor air quality, water quality, and land use.
- Disaster management: Remote sensing can be used to assess the damage caused by natural disasters, such as floods, earthquakes, and hurricanes.
-
Military applications: Remote sensing is used by the military to monitor enemy activity, plan military operations, and assess the damage caused by military operations.
-
Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, analyzing, and displaying spatial or geographic data. GIS is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
-
Land use planning: GIS can be used to map land use, identify areas of development, and assess the impact of development.
- Transportation planning: GIS can be used to map transportation networks, identify areas of congestion, and assess the impact of transportation projects.
- Environmental planning: GIS can be used to map environmental features, identify areas of environmental concern, and assess the impact of environmental projects.
- Public health: GIS can be used to map disease outbreaks, identify areas of high risk, and assess the impact of public health interventions.
-
Business: GIS can be used to map customer locations, identify areas of market potential, and assess the impact of Marketing campaigns.
-
The following are some of the benefits of using remote sensing and GIS:
-
Remote sensing and GIS can be used to collect data over large areas quickly and easily.
- Remote sensing and GIS can be used to generate maps and other visualizations that can be used to communicate information to decision-makers.
- Remote sensing and GIS can be used to analyze data and identify patterns that would not be visible from ground-based observations.
- Remote sensing and GIS can be used to monitor changes over time.
-
Remote sensing and GIS can be used to assess the impact of development projects.
-
The following are some of the challenges of using remote sensing and GIS:
-
Remote sensing and GIS can be expensive to implement and maintain.
- Remote sensing and GIS data can be difficult to interpret.
- Remote sensing and GIS data can be outdated.
- Remote sensing and GIS data can be inaccurate.
-
Remote sensing and GIS data can be biased.
-
The following are some of the ethical issues associated with using remote sensing and GIS:
-
Remote sensing and GIS can be used to invade people’s privacy.
- Remote sensing and GIS can be used to discriminate against people.
- Remote sensing and GIS can be used to exploit people.
-
Remote sensing and GIS can be used to harm the environment.
-
The following are some of the ways to address the challenges and ethical issues associated with using remote sensing and GIS:
-
Use remote sensing and GIS in a way that respects people’s privacy.
- Use remote sensing and GIS in a way that does not discriminate against people.
- Use remote sensing and GIS in a way that does not exploit people.
- Use remote sensing and GIS in a way that does not harm the environment.
- Educate people about the benefits and risks of remote sensing and GIS.
- Develop guidelines for the ethical use of remote sensing and GIS.
- Monitor the use of remote sensing and GIS to ensure that it is used in a responsible way.