Agro-climatic zones of Madhya Pradesh
There are 11 agro-climatic zones in Madhya Pradesh.
- Malwa Plateau: Indore, Dhar, (Dhar, Badnawar, Sardarpur tehsils) Shajapur, Mandsour, Nimuch, Ratlam, Ujjain, Dewas Rajgarh districts and Petlawad tehsil of Jhabua district.
- Vindhyan Plateau: Bhopal, Vidisha, Sehore (Sehore, Ashta, Ichhawar, Narsullaganj tehsils) Raisen (Raisen, Gairatganj, Begamganj, Silwani, Goharganj, Udaipura tehsils), Damoh, Guna (Chachora & Raghogarh tehsils) & Sagar districts.
3.Central Narmada Valley : Hoshangabad (Seoni-Malwa, Hoshangabad, Sohagpur tehsils), Harda, Nasinghpur districts, Budhani and Barelli tehsil of Sehore and Raisen districts respectively.
4.Satpura Plateau: Betul, Chhindwara districts.
5.Jhabua Hills: Jhabua, Jobat, Alirajpur tehsils of Jhabua district & kukshi tehsil of Dhar district.
6.Gird Region: Gwalior, Bhind, Morena, Shivpur-Kalan, Guna (Mungawali and Ashoknagar tehsils), Shivpuri (Shivpuri, Kalaras, Pohari tehsils).
7.Kymore Plateau: Jabalpur, Katni, Rewa, Panna, Satana, Sidhi, Seoni and Gopadbanas & Deosar tehsils of Sidhi district.
8.Bundel Khand Region: Tikamgarh, Chhatarpur, Datia districts, Karela, Pachore tehsil of Shivpuri and Guna tehsil of Guna district.
9.Nimar Valley: Khandwa, Khargone, Barwani district, Manawar tehsil of Dhar district and Harda district.
10.Northern Hills of Chhattisgarh: Shahdol, Umariya Mandla, Dindori district & Singrauli tehsil of Sidhi district.
11.Chhattisgarh plain: Balaghat district.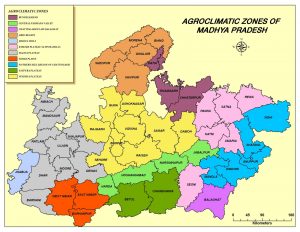
Each zone has its unique set of natural Resources and constraints. The eastern part of the State is characterized by its rice based Cropping systems, Light alfisols which have low water holding capacity and are prone to erosion mainly water erosion because of higher and often high intensity rainfall. Rainfall in this part of the state is about 1500 mm mainly received during south-west monsoon season. The central and western parts of the state follow soybean based Cropping System whereas pulses and oilseeds occupy an important place in the region. Important Soil-types/”>Soil Types in different zones of the states are mixed red and black (Kymore plateau), medium and deep black (Vindhya plateau), deep black with clay (Central Narmada Valley), Alluvial, Medium black soil, Mixed red and Black soil and red and yellow soil (Grid sub zone), clay and clay loams and sandy loam soils (Bundelkhand), light reddish brown to black clay loam (Satpura), Alluvial, Recent alluvium and Calcareous (Food Prone Eastern Plain Zone).
- Northern low lying plains comprising Gwalior, Bhind and Morena districts and extend to Bundelkhand up to the west of Panna range and excludes certain parts of Rewa district between Panna and Kaymore hills of Baghelkhand.
- The Malwa and Vindhyan Plateau comprises of Vidisha, Shivpuri, Datia, Guna, Ujjain and Mandsour districts and parts of Sehore, Raisen and Dewas districts. It consists of large undulating plains of black Cotton soil dotted with flat-topped hills. It has also hilly Vindhyan Plateau situated it the north of Narmada Valley and to the south of the low-lying regions of Bundelkhand and Baghelkhand. It separated from east of Malwa plateau to Maikal and Dorea hills of Satpura range.
- The Narmada Valley stretching from Jabalpur in the east up to Barwani district in the west. It is nearly 560 Km long and 48 Km wide and is walled on the north by the Vindhyan range and on the south by Satpura range. It covers the districts of Jabalpur, Nasinghpur, Hoshangabad, Khandwa, Khargone, Barwani, Dhar, and some parts of Raisen, Sehore, and Dewas districts.
,
Madhya Pradesh is a state in central India. It is the second-largest state in India by area, after Rajasthan. The state has a Population of over 75 million people, making it the fifth-most populous state in India. The capital of Madhya Pradesh is Bhopal.
The state is divided into 10 agro-climatic zones. These zones are:
- Zone I: Malwa plateau
- Zone II: Narmada valley
- Zone III: Chambal valley
- Zone IV: Vindhyan plateau
- Zone V: Bundelkhand plateau
- Zone VI: Eastern plateau and hills
- Zone VII: Central plateau and hills
- Zone VIII: Western plateau and hills
- Zone IX: Northern plain
- Zone X: Southern plain
Each zone has its own unique Climate and soil conditions, which make it suitable for growing different crops.
Zone I: Malwa plateau
The Malwa plateau is located in the western part of Madhya Pradesh. It is a semi-arid region with a hot summer and a cold winter. The soil is mostly sandy and loamy. The main crops grown in this zone are wheat, rice, cotton, and soybeans.
Zone II: Narmada valley
The Narmada valley is located in the central part of Madhya Pradesh. It is a fertile region with a hot summer and a mild winter. The soil is mostly alluvial. The main crops grown in this zone are rice, wheat, sugarcane, and maize.
Zone III: Chambal valley
The Chambal valley is located in the northern part of Madhya Pradesh. It is a semi-arid region with a hot summer and a cold winter. The soil is mostly sandy and loamy. The main crops grown in this zone are wheat, rice, cotton, and soybeans.
Zone IV: Vindhyan plateau
The Vindhyan plateau is located in the eastern part of Madhya Pradesh. It is a semi-arid region with a hot summer and a cold winter. The soil is mostly sandy and loamy. The main crops grown in this zone are wheat, rice, cotton, and soybeans.
Zone V: Bundelkhand plateau
The Bundelkhand plateau is located in the southeastern part of Madhya Pradesh. It is a semi-arid region with a hot summer and a cold winter. The soil is mostly sandy and loamy. The main crops grown in this zone are wheat, rice, cotton, and soybeans.
Zone VI: Eastern plateau and hills
The eastern plateau and hills are located in the eastern part of Madhya Pradesh. It is a hilly region with a hot summer and a cold winter. The soil is mostly sandy and loamy. The main crops grown in this zone are rice, wheat, maize, and pulses.
Zone VII: Central plateau and hills
The central plateau and hills are located in the central part of Madhya Pradesh. It is a hilly region with a hot summer and a cold winter. The soil is mostly sandy and loamy. The main crops grown in this zone are rice, wheat, maize, and pulses.
Zone VIII: Western plateau and hills
The western plateau and hills are located in the western part of Madhya Pradesh. It is a hilly region with a hot summer and a cold winter. The soil is mostly sandy and loamy. The main crops grown in this zone are rice, wheat, maize, and pulses.
Zone IX: Northern plain
The northern plain is located in the northern part of Madhya Pradesh. It is a fertile region with a hot summer and a mild winter. The soil is mostly alluvial. The main crops grown in this zone are rice, wheat, sugarcane, and maize.
Zone X: Southern plain
The southern plain is located in the southern part of Madhya Pradesh. It is a fertile region with a hot summer and a mild winter. The soil is mostly alluvial. The main crops grown in this zone are rice, wheat, sugarcane, and maize.
The agro-climatic zones of Madhya Pradesh are important for the state’s economy. The state is a major producer of agricultural products, including rice, wheat, cotton, and soybeans. The agro-climatic zones provide the state with a diverse range of crops that can be grown in different climates and soil conditions. This diversity helps to ensure that the state’s economy is not reliant on any one crop or region.
What is a climate zone?
A climate zone is a large area of the Earth’s surface that has similar climate conditions. Climate zones are determined by factors such as latitude, altitude, and proximity to water.
What are the different Types of Climate zones?
There are many different types of climate zones, but some of the most common include tropical, temperate, and polar. Tropical climate zones are characterized by warm temperatures and high rainfall. Temperate climate zones have moderate temperatures and rainfall. Polar climate zones are characterized by cold temperatures and low rainfall.
What are the characteristics of each climate zone?
The characteristics of each climate zone vary depending on the factors that determine it. For example, tropical climate zones are typically characterized by warm temperatures, high rainfall, and lush vegetation. Temperate climate zones are typically characterized by moderate temperatures, moderate rainfall, and a variety of plant and animal life. Polar climate zones are typically characterized by cold temperatures, low rainfall, and sparse vegetation.
What are the benefits of living in a particular climate zone?
The benefits of living in a particular climate zone vary depending on the individual’s preferences. For example, people who enjoy warm weather may prefer to live in a tropical climate zone. People who enjoy moderate weather may prefer to live in a temperate climate zone. People who enjoy cold weather may prefer to live in a polar climate zone.
What are the challenges of living in a particular climate zone?
The challenges of living in a particular climate zone also vary depending on the individual’s preferences. For example, people who live in tropical climate zones may have to deal with high temperatures and humidity. People who live in temperate climate zones may have to deal with extreme weather events such as hurricanes and tornadoes. People who live in polar climate zones may have to deal with extreme cold and snow.
What are some examples of climate zones?
Some examples of climate zones include the tropical rainforest, the temperate Grassland, and the polar Tundra. The tropical rainforest is a climate zone that is characterized by warm temperatures, high rainfall, and lush vegetation. The temperate grassland is a climate zone that is characterized by moderate temperatures, moderate rainfall, and a variety of plant and animal life. The polar tundra is a climate zone that is characterized by cold temperatures, low rainfall, and sparse vegetation.
What are the effects of Climate Change on climate zones?
Climate change is causing the Earth’s climate to change at an unprecedented rate. This is having a significant impact on climate zones around the world. For example, some climate zones are becoming warmer, while others are becoming cooler. This is causing changes in plant and animal life, as well as changes in human activity.
What are some ways to adapt to climate change?
There are many ways to adapt to climate change. Some of the most common include:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This is the most important way to address climate change. Greenhouse gas emissions are the main cause of climate change, so reducing them will help to slow the rate of change.
- Adapting to the impacts of climate change. This includes measures such as building sea walls to protect coastal areas from rising sea levels, and developing drought-resistant crops to cope with changing rainfall patterns.
- Investing in RENEWABLE ENERGY sources. Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power do not produce greenhouse gases, so they can help to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
- Educating people about climate change. The more people who understand climate change, the more likely we are to take action to address it.
What are the future of climate zones?
The future of climate zones is uncertain. Climate change is causing the Earth’s climate to change at an unprecedented rate, and this is having a significant impact on climate zones around the world. It is possible that some climate zones will disappear altogether, while others may merge or shift. It is also possible that new climate zones will emerge.
Sure, here are some MCQs on the topics of climate, weather, and agriculture:
-
Which of the following is not a type of climate?
(A) Tropical
(B) Temperate
(C) Polar
(D) Agro-climatic -
The Average temperature in a tropical climate is:
(A) Warm
(B) Cool
(C) Cold
(D) Hot -
The average temperature in a temperate climate is:
(A) Warm
(B) Cool
(C) Cold
(D) Hot -
The average temperature in a polar climate is:
(A) Warm
(B) Cool
(C) Cold
(D) Hot -
Agriculture is the practice of:
(A) Raising Livestock
(B) Growing crops
(C) Both raising livestock and growing crops
(D) None of the above -
Which of the following is not a type of agriculture?
(A) Subsistence agriculture
(B) Commercial agriculture
(C) Agro-climatic agriculture
(D) Industrial agriculture -
Subsistence agriculture is a type of agriculture in which:
(A) Farmers grow crops and raise livestock to meet their own needs
(B) Farmers grow crops and raise livestock to sell for profit
(C) Farmers grow crops and raise livestock to both meet their own needs and sell for profit
(D) None of the above -
Commercial agriculture is a type of agriculture in which:
(A) Farmers grow crops and raise livestock to meet their own needs
(B) Farmers grow crops and raise livestock to sell for profit
(C) Farmers grow crops and raise livestock to both meet their own needs and sell for profit
(D) None of the above -
Industrial agriculture is a type of agriculture in which:
(A) Farmers grow crops and raise livestock to meet their own needs
(B) Farmers grow crops and raise livestock to sell for profit
(C) Farmers grow crops and raise livestock to both meet their own needs and sell for profit
(D) Farmers use large-scale machinery and technology to grow crops and raise livestock on a large scale. -
Which of the following is not a benefit of agriculture?
(A) It provides food for people
(B) It provides jobs for people
(C) It helps to regulate the climate
(D) It pollutes the Environment -
Which of the following is not a challenge of agriculture?
(A) Soil erosion
(B) Water Pollution
(C) Air Pollution
(D) Climate change -
Which of the following is a way to reduce soil erosion?
(A) Plant trees
(B) Use cover crops
(C) Practice no-till farming
(D) All of the above -
Which of the following is a way to reduce water pollution?
(A) Use drip Irrigation
(B) Install a water treatment system
(C) Recycle water
(D) All of the above -
Which of the following is a way to reduce air pollution?
(A) Use renewable energy sources
(B) Plant trees
(C) Reduce your reliance on cars
(D) All of the above -
Which of the following is a way to mitigate climate change?
(A) Reduce your carbon footprint
(B) Plant trees
(C) Invest in renewable energy sources
(D) All of the above
I hope these MCQs were helpful! Let me know if you have any other questions.